Pain, stiffness, and slow recovery can make everyday life harder than it should be. For people dealing with injury, ongoing discomfort, or limited movement, finding real relief is a top priority. Electrotherapy is a gentle, proven method used in physiotherapy to ease pain, support healing, and help the body move better. By using low-level electrical currents to target nerves and muscles it plays a valuable role in recovery and rehabilitation.
What Is Electrotherapy?
Electrotherapy involves applying mild electrical currents to the body through electrodes placed on the skin. These impulses interact with the nervous system and muscles, triggering responses that can block pain signals, stimulate muscle contractions, and improve blood flow.
Unlike invasive treatments, electrotherapy is painless, easy to administer, and generally free from major side effects, making it a preferred option among physiotherapists.
A Brief History of Electrotherapy
While today’s electrotherapy uses advanced technology, its roots go back to ancient times. In ancient Rome, electric fish were used to relieve pain. Scientific exploration began in the 18th century and has since evolved into the evidence-based modalities now widely used in modern physiotherapy.
How Electrotherapy Works
Electrotherapy delivers controlled electrical currents or magnetic fields to specific areas of the body. These signals interact with the nervous system to:
- Block or alter pain signal transmission to the brain
- Stimulate the release of endorphins (natural painkillers)
- Promote muscle contractions to prevent atrophy
- Improve blood circulation and nutrient delivery
- Accelerate tissue repair and collagen production
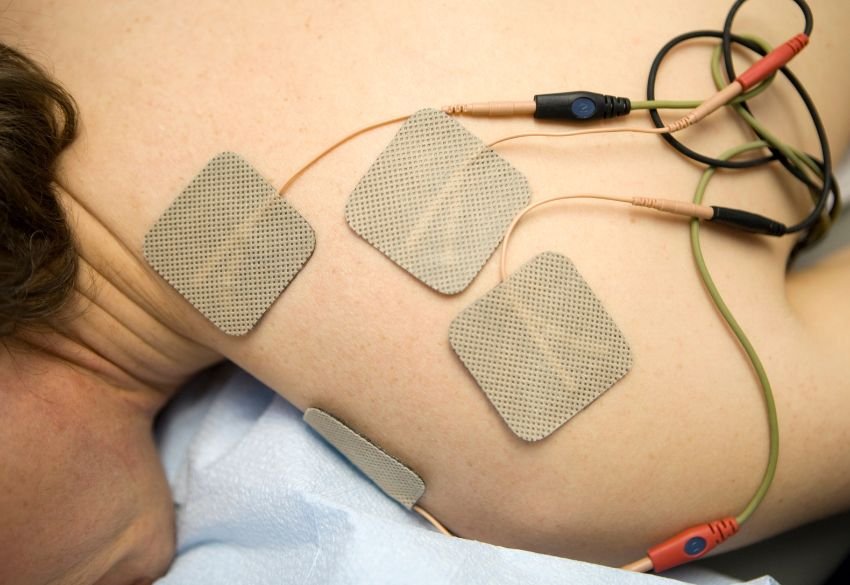
Common Types of Electrotherapy
| Modality | Description | Typical Use |
| TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) | Delivers low-voltage impulses to sensory nerves via surface electrodes | Chronic pain, arthritis, neuropathy |
| EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation) | Induces controlled muscle contractions | Muscle strengthening, re-education |
| Interferential Therapy (IFC) | Uses medium-frequency currents to reach deeper tissues | Pain relief, inflammation reduction |
| PENS (Percutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) | Combines acupuncture with electrical impulses | Nerve-related pain |
| Shockwave Therapy | Uses acoustic waves to stimulate tissue regeneration | Tendinopathies, plantar fasciitis |
| Ultrasound Therapy | Generates mechanical vibrations through sound waves | Inflammation, soft tissue injury |
| rTMS (Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation) | Uses magnetic pulses to stimulate the brain | Chronic pain, neurological and mood disorders |
| Electroacupuncture | Electrical impulses are delivered through acupuncture needles | Enhanced pain relief |
Clinical Benefits of Electrotherapy
Electrotherapy offers multiple therapeutic benefits that contribute to improved patient outcomes. These include:
Pain Reduction
Electrotherapy can interrupt pain pathways and desensitise nerves, helping to manage both acute and chronic pain conditions. It also promotes the release of endorphins, providing a natural analgesic effect.
Reduced Inflammation and Swelling
Certain modalities enhance circulation and lymphatic drainage, which can reduce inflammation and accelerate recovery after injury or surgery.
Improved Muscle Function
EMS helps strengthen weakened muscles, restore coordination, and improve functional movement. This is particularly beneficial in postoperative rehabilitation or neurological recovery.
Tissue Healing
Enhanced blood flow delivers oxygen and nutrients to support tissue repair and reduce complications.
Restored Mobility and Function
By reducing pain and improving muscle control, electrotherapy can facilitate a greater range of motion, joint stability, and physical performance.

Conditions Commonly Treated with Electrotherapy
Electrotherapy is widely used in physiotherapy to help treat a variety of musculoskeletal and neurological conditions. Its versatility makes it useful in both early-stage recovery and long-term rehabilitation. It is an effective way to manage pain, support healing, and improve movement across many different types of injuries and health concerns:
- Back and neck pain
- Arthritis (osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis)
- Tendon injuries (e.g., Achilles tendinopathy, rotator cuff tears)
- Nerve-related pain (e.g., sciatica, diabetic neuropathy)
- Sports injuries (strains, sprains, overuse injuries)
- Post-surgical recovery (e.g., joint replacements, ligament repairs)
- Fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome
- Stroke rehabilitation and neurological dysfunction
What the Research Says
While long-term effects may vary, the short- to medium-term results are well documented, particularly when electrotherapy is used in combination with manual therapy, exercise, and education.
Clinical studies support the effectiveness of electrotherapy in physiotherapy. For example, a 2017 randomised trial on chronic low back pain patients showed that interferential current therapy significantly reduced pain scores from an average of 7.56 to 0.97 on the Visual Analogue Scale, along with improved hip mobility. Similarly, a 2023 systematic review found that TENS therapy effectively reduced pain intensity and tenderness in patients with temporomandibular disorders compared to placebo treatments.
Safety and Considerations
Electrotherapy is considered safe when administered by a trained physiotherapist. Side effects are rare and typically limited to temporary skin irritation. However, it may not be suitable for individuals who:
- Have pacemakers or implanted defibrillators
- Have open wounds, infections, or burns at the treatment site
- Are pregnant (depending on the case)
- Have a history of seizures (modality-dependent)
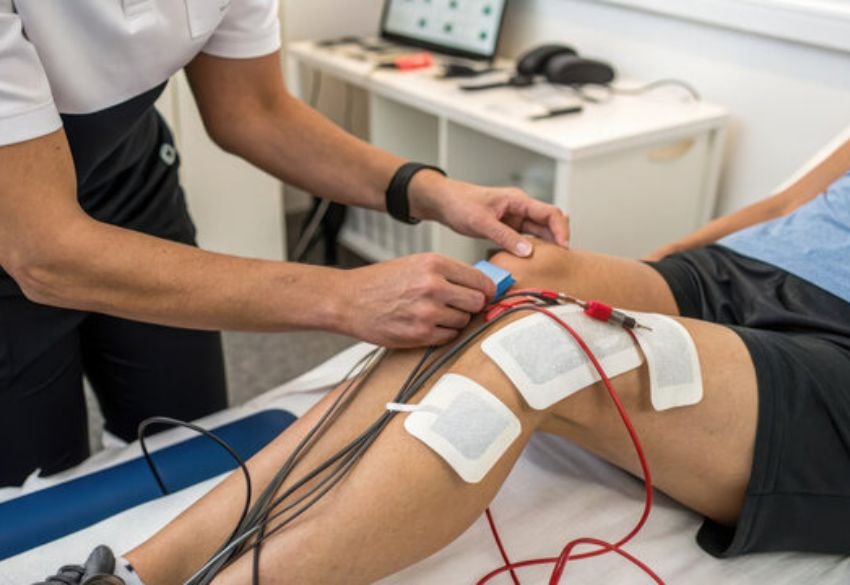
What to Expect During a Session
A typical session involves placing electrodes on the skin near the problem area. The physiotherapist adjusts the intensity and frequency of the electrical impulses based on your condition and comfort level.
- Most patients feel a tingling or pulsing sensation, usually comfortable
- No downtime is required, and normal activities can resume immediately after
Integrating Electrotherapy into Your Recovery Plan
Electrotherapy works best when combined with other physiotherapy methods such as manual therapy, exercise, and movement education. A holistic approach ensures not only symptom relief but also long-term recovery and prevention of future issues.
At Mickleham Physio, electrotherapy is integrated into personalised treatment plans tailored to your unique goals and health needs. With advanced technology and skilled practitioners, we provide effective, non-invasive care that helps patients heal faster, move better, and return to the life they love.
If you’re interested in exploring how electrotherapy can help you, contact us for a thorough assessment and customised therapy plans to maximise your recovery and improve your quality of life.

