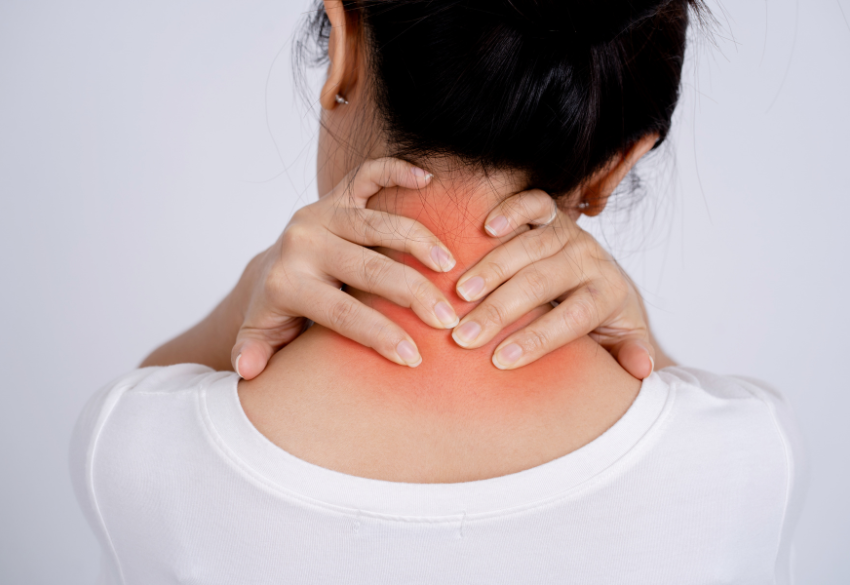
Head and neck conditions can affect vital functions like breathing, swallowing, speech, and movement. They can stem from infections, structural abnormalities, tumours, nerve issues, or repetitive strain. These issues often involve the muscles, bones, nerves, and soft tissues in the upper spine, skull, and face. While some of these are temporary and easily treatable, others may require long-term care or even surgery. Understanding the most common head and neck problems—and what causes them—can help people seek treatment sooner and avoid complications.
How Common Are These Problems?
Head and neck problems are surprisingly common and can range from minor annoyances to serious, life-altering conditions. Recent studies and health data reveal that:
- Up to 70% of people will experience neck pain at least once in their lives.
- In Australia specifically, 10% to 20% of the population is suffering from neck pain at any given time.
- Women and individuals aged around 45 are more likely to be affected.
- National figures show a prevalence rate of about 1,093 cases per 100,000 people (age-standardised), with around 246 new cases per 100,000 Australians reported each year.
Neck pain ranks among the top reasons for medical consultations, work absenteeism, and disability. It’s especially common in office-based professions, where extended periods of sitting and poor posture can trigger chronic discomfort.
Common Causes of Head and Neck Problems
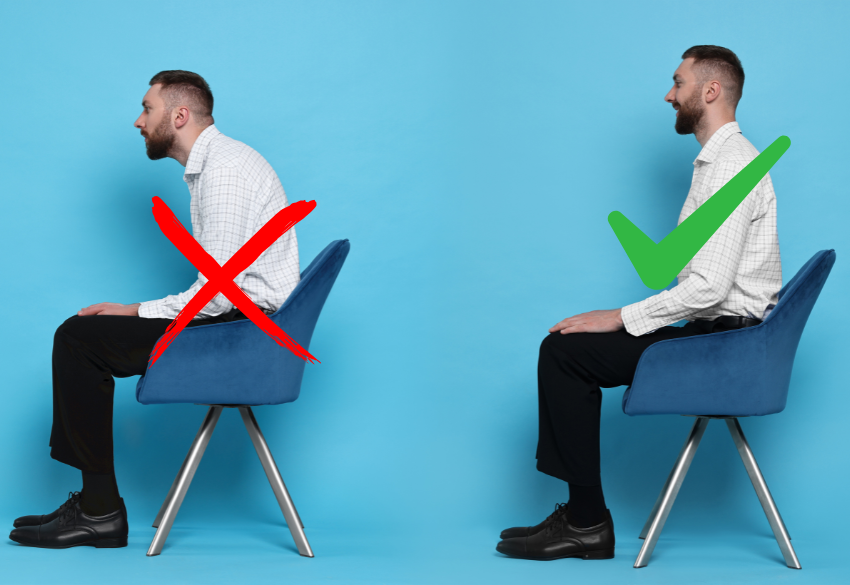
- Poor Posture
One of the most significant contributors to head and neck problems is poor posture. People spend hours each day looking down at smartphones, tablets, or working at computers. This forward head posture places excessive strain on the neck muscles and cervical spine.
- Muscle Strain and Overuse
Repetitive movements or holding the head in one position for extended periods can cause muscle strain. Activities such as typing, sewing, driving, or even poor sleeping positions can lead to tight, overworked neck and shoulder muscles. This tension often results in discomfort, stiffness, and sometimes referred pain to the head, causing tension-type headaches.
- Injuries and Trauma
Whiplash injuries from car accidents, falls, or sports can damage the soft tissues of the neck, leading to chronic pain and stiffness. Even minor injuries can disrupt normal neck function and cause headaches.
- Degenerative Changes
As people age, degenerative changes such as osteoarthritis and disc degeneration can affect the cervical spine. These changes may cause joint inflammation, nerve compression, and chronic neck pain. Bone spurs or herniated discs can irritate nerves, leading to radiating pain and headaches.

- Stress and Psychological Factors
Stress and anxiety contribute significantly to muscle tension in the neck and shoulders. This tension can trigger or worsen headaches and neck pain. Emotional stress often leads to poor posture and increased muscle guarding, creating a vicious cycle of pain.
- Other Medical Conditions
Less commonly, neck pain and headaches may be symptoms of underlying medical conditions such as infections (e.g., meningitis), inflammatory diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis), or neurological disorders.
Common Head and Neck Conditions
Here’s a breakdown of the most frequently seen problems in this area:
- Neck Pain
Symptoms: Stiffness, muscle spasms, limited range of motion, sometimes radiating pain down the arms.
Causes: Poor posture (especially with prolonged device use), degenerative changes in the spine, injuries, and muscle strain.
- Head and Neck Cancers
Symptoms: Persistent sore throat, hoarseness, swelling in the neck, difficulty swallowing or breathing, sores that don’t heal.
Causes: Tobacco use, alcohol consumption, HPV infection, and occupational exposure to certain chemicals or dust.
- Occipital Neuralgia
Symptoms: Sharp, stabbing pain that starts at the base of the skull and can radiate to the scalp or behind the eyes.
Causes: Nerve irritation or injury, often from trauma, tight muscles, or spinal disc issues.
- Salivary Gland Disorders
Symptoms: Facial swelling (especially near the jaw), dry mouth, facial numbness, or persistent pain.
Causes: Infections, blocked ducts, or tumours—both benign and malignant.
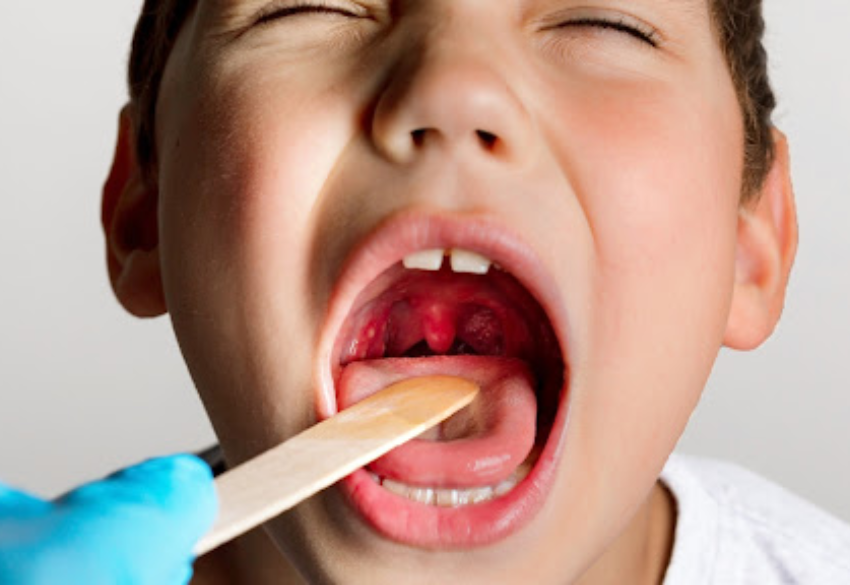
- Tonsillitis and Adenoiditis
Symptoms: Sore throat, difficulty swallowing, fever, swollen glands in the neck.
Causes: Bacterial or viral infections, most common in children.
- Chronic Sinusitis
Symptoms: Ongoing nasal congestion, facial pressure, reduced sense of smell, postnasal drip.
Causes: Allergies, nasal polyps, or structural problems like a deviated septum.
- Anterior Head Translation
Symptoms: Forward head posture, neck and upper back pain, muscle fatigue.
Causes: Often due to poor posture from sitting at a desk or using screens for long periods.
The Role of Physiotherapy in Managing Head and Neck Problems
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in treating head and neck issues by addressing the root causes rather than just masking symptoms. Key physiotherapy approaches include:
- Postural Assessment and Correction: Identifying poor posture habits and educating clients on how to maintain a neutral spine during daily activities.
- Manual Therapy: Hands-on techniques to relieve muscle tension, improve joint mobility, and reduce pain.
- Targeted Exercise Programs: Strengthening weak muscles and stretching tight ones to restore balance and support the neck.
- Ergonomic Advice: Guidance on workstation setup, sleeping positions, and lifestyle modifications to prevent recurrence.
- Pain Management Strategies: Including heat/cold therapy, dry needling, and relaxation techniques.
Tips to Prevent Head and Neck Problems
While physiotherapy can effectively treat existing problems, prevention is equally important. Here are some practical tips:
- Maintain good posture—keep your head aligned over your shoulders.
- Take regular breaks from sitting or screen time; stretch and move frequently.
- Set up your workstation ergonomically, with your monitor at eye level.
- Avoid cradling your phone between your ear and shoulder.
- Use supportive pillows and sleep in positions that maintain neck alignment.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, or mindfulness.

When to See a Physiotherapist
If you experience persistent neck pain, frequent headaches, stiffness, or reduced neck movement that affects your daily life, it’s time to seek professional help. Early intervention can prevent symptoms from worsening and reduce the risk of chronic pain.
At Mickleham Physio, you’ll receive a thorough assessment and a personalised treatment plan designed to restore function, relieve pain, and improve your quality of life.
We offer effective, evidence-based solutions to treat and prevent head and neck problems. By addressing posture, muscle imbalances, and ergonomic factors, physiotherapists at Mickleham Physio help clients find lasting relief and return to pain-free living.
If you’re struggling with neck pain or headaches, don’t wait—contact us and explore the expert physiotherapy services available at Mickleham Physio and take the first step toward a healthier, more comfortable life.